The abnormal growth of skin cells , most often develops on skin exposed to the sun. But this common form of cancer can also occur on areas of your skin not ordinarily exposed to sunlight.
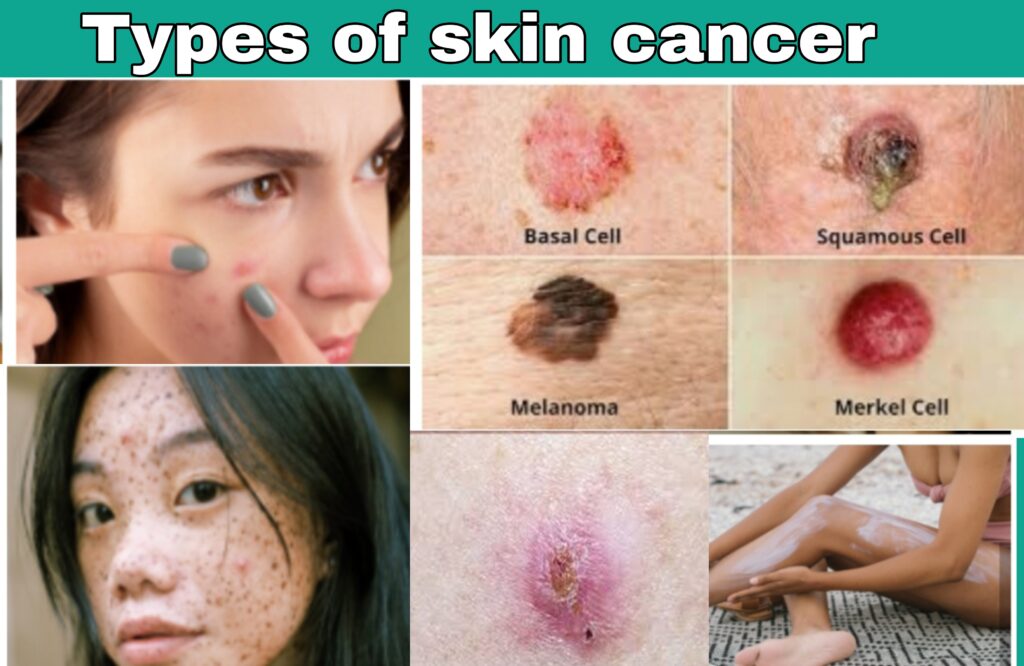
There are three major types of skin cancer — basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma and melanoma.
You can reduce your risk of skin cancer by limiting or avoiding exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation. Checking your skin for suspicious changes can help detect skin cancer at its earliest stages. Early detection of skin cancer gives you the greatest chance for successful skin cancer treatment.
Where skin cancer develops
Skin cancer develops primarily on areas of sun-exposed skin, including the scalp, face, lips, ears, neck, chest, arms and hands, and on the legs in women. But it can also form on areas that rarely see the light of day — your palms, beneath your fingernails or toenails, and your genital area.
Skin cancer affects people of all skin tones, including those with darker complexions. When melanoma occurs in people with dark skin tones, it’s more likely to occur in areas not normally exposed to the sun, such as the palms of the hands and soles of the feet.
What are the 4 signs of skin cancer?
Redness or new swelling beyond the border of a mole. Color that spreads from the border of a spot into surrounding skin. Itching, pain, or tenderness in an area that doesn’t go away or goes away then comes back. Changes in the surface of a mole: oozing, scaliness, bleeding, or the appearance of a lump or bump.
What are the 7 warning signs of skin cancer?
- Changes in Appearance. …
- Post-Mole-Removal changes to your skin. …
- Fingernail and Toenail changes. …
- Persistent Pimples or Sores. …
- Impaired Vision. …
- Scaly Patches. …
- Persistent Itching.
What are the early stages of skin cancer?
Skin cancer may initially appear as a nodule, rash or irregular patch on the surface of the skin. These spots may be raised and may ooze or bleed easily. As the cancer grows, the size or shape of the visible skin mass may change and the cancer may grow into deeper layers of the skin.
How long do you live with skin cancer?
The overall average 5-year survival rate for all patients with melanoma is 92%. This means 92 of every 100 people diagnosed with melanoma will be alive in 5 years. In the very early stages the 5-year survival rate is 99%. Once melanoma has spread to the lymph nodes the 5-year survival rate is 63%.
At what age does skin cancer typically occur?
Age. Most basal cell and squamous cell carcinomas typically appear after age 50. However, in recent years, the number of skin cancers in people age 65 and older has increased dramatically. This may be due to better screening and patient tracking efforts in skin cancer.
Are skin cancers itchy?
Yes, skin cancer can be itchy. For example, basal cell skin cancer can appear as a crusty sore that itches. The deadliest form of skin cancer — melanoma — can take the form of itchy moles. See your doctor for any itchy, crusty, scabbed, or bleeding sore that’s not healing.
Who is most at risk for skin cancer?
- A lighter natural skin color.
- Skin that burns, freckles, reddens easily, or becomes painful in the sun.
- Blue or green eyes.
- Blond or red hair.
- Certain types and a large number of moles.
- A family history of skin cancer.
- A personal history of skin cancer.
- Older age.
Can you get skin cancer with no sun exposure?
Skin cancer , the abnormal growth of skin cells , most often develops on skin exposed to the sun. But this common form of cancer can also occur on areas of your skin not ordinarily exposed to sunlight.
Can skin cancer look like a pimple?
In particular, a serious form of skin cancer called nodular melanoma can often look very similar to a pimple. Nodular melanomas are a firm, raised bump which are usually red, brown or skin coloured. They can sometimes be misdiagnosed as a harmless pimple.
Is skin cancer painful to touch?
In the case of melanoma, a painless mole may start getting tender, itchy, or painful. Other skin cancers generally do not hurt to touch until they have advanced to become large. The peculiar absence of pain in a skin sore or a rash often directs the diagnosis toward skin cancer.
Does skin cancer bleed if you pick it?
It is not uncommon for spots on our skin to bleed after being itched or picked at, but, if you have a spot that bleeds in the middle of the night, when you are washing your face, or when it is lightly bumped, you should consider seeing your dermatologist as soon as possible.
What happens if you leave skin cancer untreated?
However, left untreated, BCCs can grow deeper into the skin and damage surrounding skin, tissue, and bone. Occasionally, a BCC can become aggressive, spreading to other parts of the body and even becoming life threatening.
Can skin cancer make you feel tired?
Cancer uses your body’s nutrients to grow and advance, so those nutrients are no longer replenishing your body. This “nutrient theft” can make you feel extremely tired.
Can you lose weight with skin cancer?
Unintentional weight loss is a common side effect of any cancer. When it comes to melanoma, extreme weight loss usually only happens after the cancer has spread from the skin to other parts of the body.
Where does skin cancer spread to first?
Normally, the first place a melanoma tumor metastasizes to is the lymph nodes, by literally draining melanoma cells into the lymphatic fluid, which carries the melanoma cells through the lymphatic channels to the nearest lymph node basin.
Does skin cancer cause back pain?
Melanoma is a type of skin cancer. Melanoma that has gone undetected and spread through the body can spread to the spine, causing back pain.
Diagnosing skin cancer
Skin cancer is diagnosed with a skin biopsy, which involves removing a sample of the suspicious tissue for examination under a microscope. If your skin cancer is large or deep, or if it has spread to other parts of your body, you may need more tests, including a sentinel lymph node biopsy, which shows whether a melanoma has spread to your lymph nodes. You may also require X-rays, CT, MRI, or PET scans.
Skin cancer symptoms & treatment
Skin cancer (also referred to as melanoma) is a tumor or growth of abnormal cells on the skin, your body’s largest organ. These skin tumors can be benign (noncancerous) or malignant (cancerous). There are three types of skin cancer:
- Basal cell carcinoma is the most common type. It typically occurs on the surface layer of your skin.
- Squamous cell carcinoma is the second most common type and it also develops on the outer layers of skin.
- Malignant melanoma is the most serious type, since it’s more likely to spread beneath the skin. It can be life threatening: 10,000 people will die this year from melanoma.
Although skin cancer is the most common form of cancer, your skin has an incredible capacity to heal and regenerate. Skin cancer is often treatable, especially if caught early. Our skin cancer specialists offer cutting-edge, compassionate care at clinics in Milwaukee, Sheboygan, and throughout eastern Wisconsin and northern Illinois.
Symptoms of skin cancer
Skin cancer symptoms vary depending on the type of skin cancer that’s causing them.
Basal cell carcinoma often looks like a small, dome-shaped pimple, with a pearly color. You might see blood vessels on the surface. In other cases, basal cell carcinomas may look like a pink, shiny patch or a sore that doesn’t heal.
Squamous cell carcinoma usually looks like a red, crusty or scaly patch, a sore or a firm red bump. You’ll usually see these signs on skin that’s been exposed to the sun.
Malignant melanoma often develops in or near a mole. Typical melanoma symptoms include a mole that is painful, itchy or bleeding, or a mole that has changed shape, color or size.
When examining your atypical moles, remember the rule of “ABCDE”:
- Asymmetry: Is each side of the mole shaped differently?
- Border: Are the mole’s edges ragged or blurred?
- Color: Is the mole uneven shades of brown, black, tan, red, white or blue?
- Diameter: Is the mole larger than the tip of a pencil eraser?
- Enlargement: Has the mole increased in size?
- Evolution: Does the mole look different than the other moles around it or is it changing size, shape or color.
Treatment options for skin cancer
If you’re diagnosed with melanoma, your doctor will evaluate how deep the tumor has grown into your skin and how far it has spread in your body. Once the depth has been determined, your doctor can develop a personalized plan for skin cancer treatment. Sometimes, a biopsy can remove all of the cancerous tissue, and no further treatment is necessary. In most cases, though, you’ll need to have the lesion – and part of the normal skin around it – removed.Removal can be done using a variety of techniques: freezing, scraping and burning, excision and radiation therapy. Some of these techniques can be performed right in your doctor’s office, using a local anesthetic. Other skin cancer treatment options include:
- Mohs micrographic surgery: Your doctor precisely removes only the cancerous tissue.
- Surgery: Larger growths may require more extensive surgery to remove. In some cases, your doctor may need to use flaps or grafts of skin to improve your appearance afterwards.
- Radiation therapy: This procedure uses highly advanced technology to destroy skin cancer cells or to prevent them from growing.
- External beam radiation: This is usually used to treat melanoma that has spread to other organs.
- Immunotherapy: This treatment stimulates your immune system to identify and destroy cancer cells, without affecting healthy tissue.
- Clinical trials: If you have Stage 3 or Stage 4 melanoma, you may want to consider clinical trials — research studies in which scientists test potential new cures — as a treatment option.
Prevention of skin cancer
It’s easier to prevent skin cancer than any other type of cancer – yet the number of cases continues to grow. In the U.S., more than 3.5 million cases are diagnosed every year. That’s more than breast, prostate, lung and colon cancers combined. Experts predict that one in five Americans will develop skin cancer in his or her lifetime.
People of all skin colors and races can develop melanoma; however, those at the highest risk are people with fair skin and blue eyes, those who sunburn easily and those who have a lot of freckles. Additional risk factors include previous sunburns, a family history of skin cancer, a weakened immune system, scarring on your skin caused by a disease, and exposure to X-rays, tanning beds or sunlamps, or to cancer-causing compounds (such as arsenic).
Ultraviolet (UV) rays from the sun damage your skin and, over time, lead to skin cancer. The best way to protect yourself is to avoid too much sun exposure – especially sunburns. Here’s how to prevent skin cancer by avoiding the sun:
- Avoid direct sunlight for long periods of time, especially between 10 a.m. and 4 p.m.
- Wear a hat with a wide brim to protect your face and ears and long-sleeved shirts and pants.
- Use a broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF (sun protection factor) of 30 or higher.
- Apply sunscreen 30 minutes before you go out in the sun and reapply often – especially when swimming or sweating.
- Wear sunglasses with UVA protection to shield your eyes and use a lip balm with sunscreen to protect your lips.
- Don’t use tanning beds or sunlamps.
I hope you liked this article.
Thanking you!!