Measles (Rubeola) & Koplik’s Spot:
Measles (Rubeola) is a common infectious disease especially among children, in which your body feels hot and your skin is covered in small red spots. Measles causitive agent is paramyxovirus. Measles (also known as rubeola, coughing measles, hard measles, morbilli, red measles, and 10-day measles) is an infection that is easily spread from one person to another. It is caused by a virus that is transmitted via person to person contact as well as airborne spread. Measles most often affected preschooler between 4 and 5 years of age. In Measles “Koplik’s Spot” are seen in children. Koplik’s Spot mean: (Tiny white spots with bluish-white centers on a red background found inside the mouth on the inner lining of the cheek (buccal cavity) — also called Koplik’s spots).
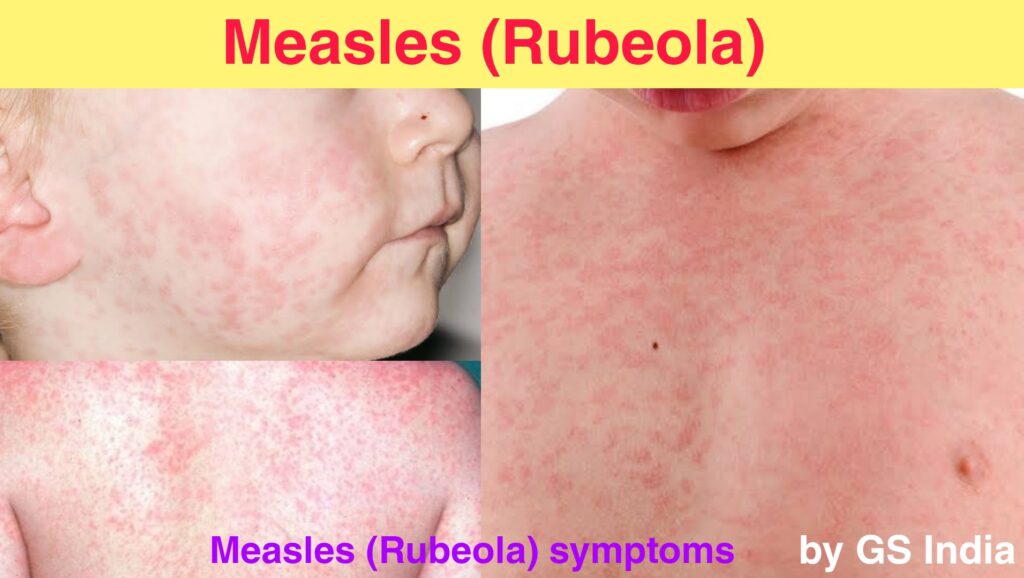
Common Sign and Symptoms of Measles (Rubeola):
Common sign and symptoms are included in measles (rubeola):skin rash, dry cough, pink eye, diarrhoea, headache, koplik’s spots, sensitivity to light, sore throat, or swollen lymph nodes.
They include cough, runny nose, inflamed eyes, sore throat, fever and a red, blotchy skin rash. Measles infection can last for several weeks. Symptoms usually start 7 to 14 days after someone is exposed to the virus.
People may experience ‘: Pain areas: in the muscles
Whole body: fever, malaise, or loss of appetite, fatigue.
Nasal areas: runny nose or sneezing.
Measles Stages (Rubeola Stages)
Measles can be divided into three stages:
1- Prodromal stage, 2-Eruptive stage, 3- Convalescent stage, and should be suspected in patient with the classic triad of three “Cs” Cough, Conjunctives and Coryza.
The primary or prodormal phase last four to six days and is characterized by the persons of high fever, malaise, coryza, Conjunctivitis, palpebral edema and dry cough. In most cases so the characteristic “Koplik Spots” of the disease located in the buccal mucosa at the height of the second molar and appear to the three days before the rashes and disappear on the third day.
Prevention and Treatment of Measles (Rubeola):
Measles can be prevented with measles vaccine (MMR vaccine). Health care providers recommend that children receive the MMR vaccine between 12 and 15 month of age and again between 4 and 6 year of age before entering school. The MMR vaccine to doses are 97% effective in preventive Measles and protecting against it for life.
There is no specific medical treatment for measles. To help manage symptoms-
- Encourage extra rest
- The best way to protect your kids is to make sure they are immunised against measles.
- Give your child plenty of fluids.
- Give a non-aspirin fever medicine, such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen. Note– if a fever makes your child uncomfortable never give aspirin to a child.
What is difference between Rubella and Rubeola?
–Rubella, also known as German measles, is an infection by the rubella virus. Rubeola, often referred to simply as measles, is an infection by a virus in the paramyxoviridae family. Both are highly contagious airborne viruses. That means they spread through tiny droplets in the air, like in a cough or sneeze. Rubeola, also called 10-day measles, red measles, or measles, is a viral illness that results in a viral exanthem (rashes or skin eruption).
Thanks!! By GS India Nursing!!